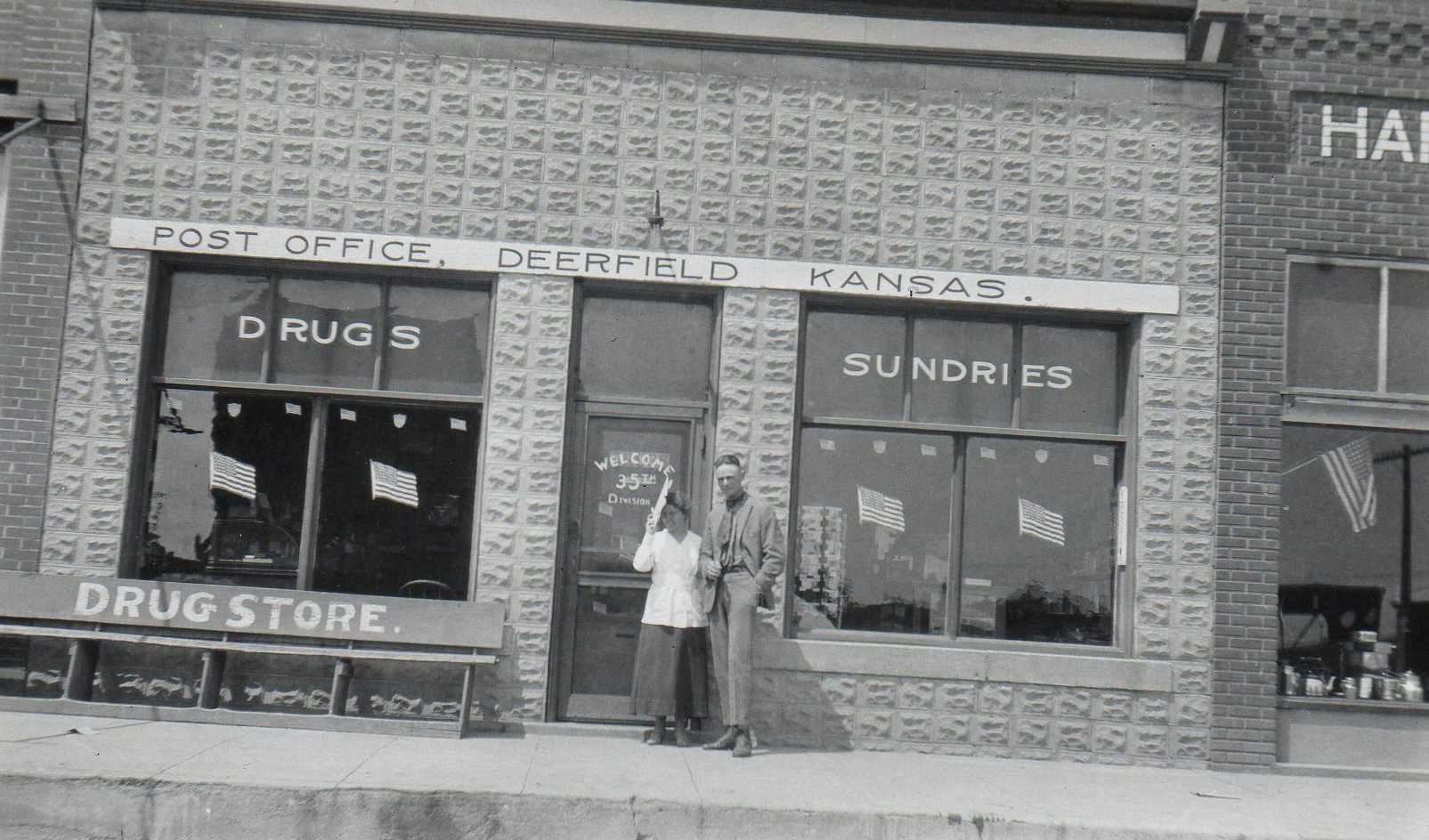
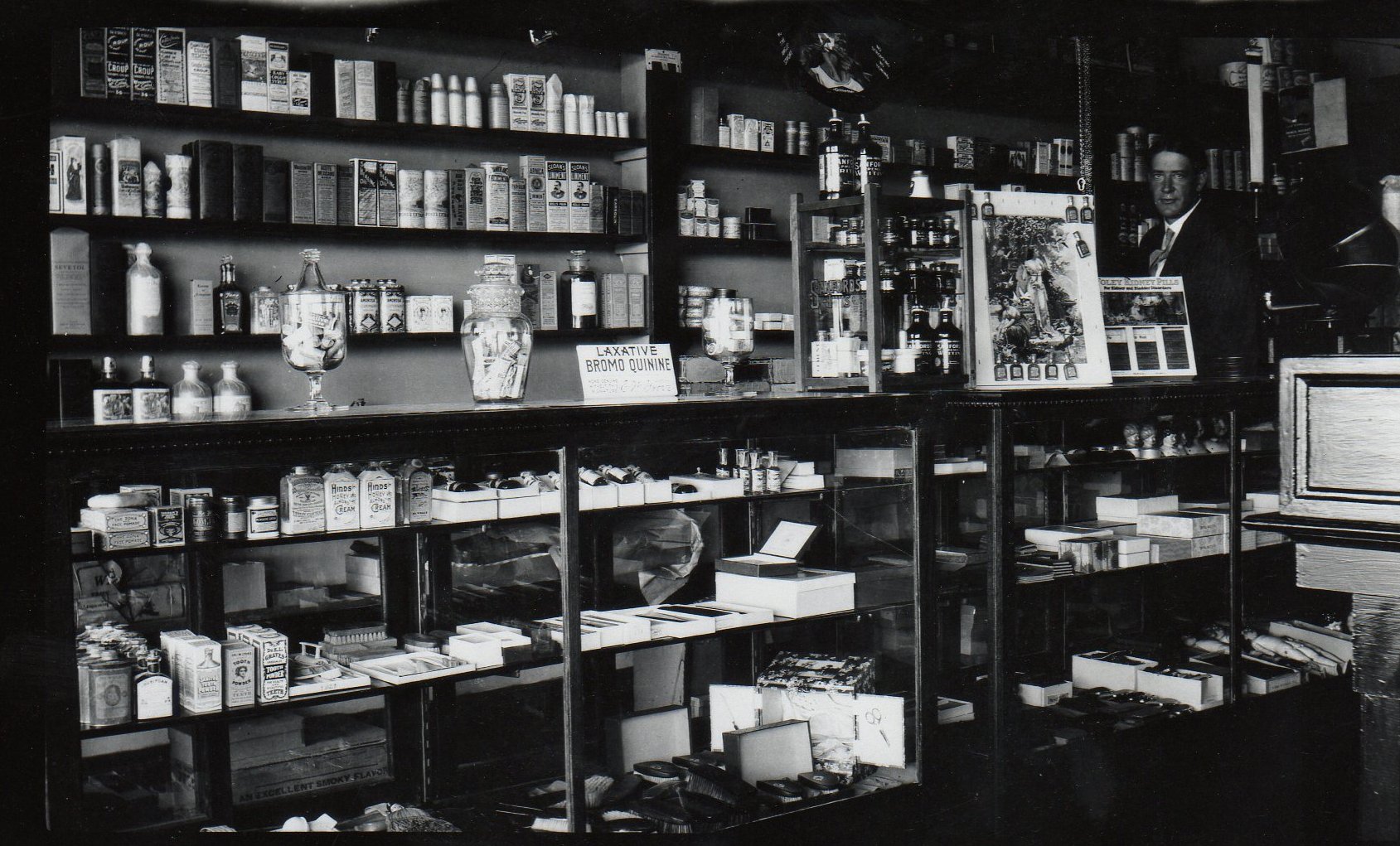
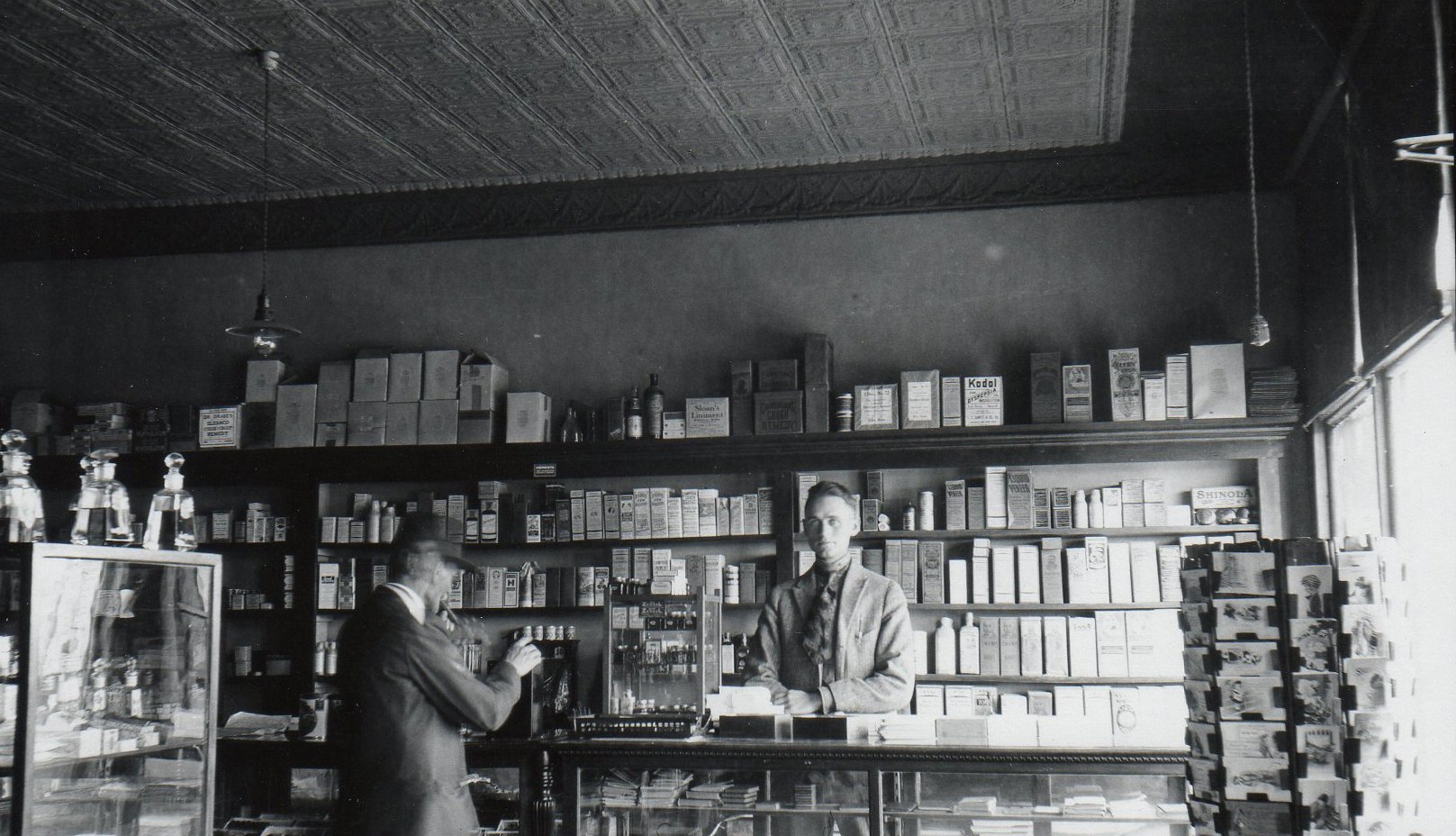
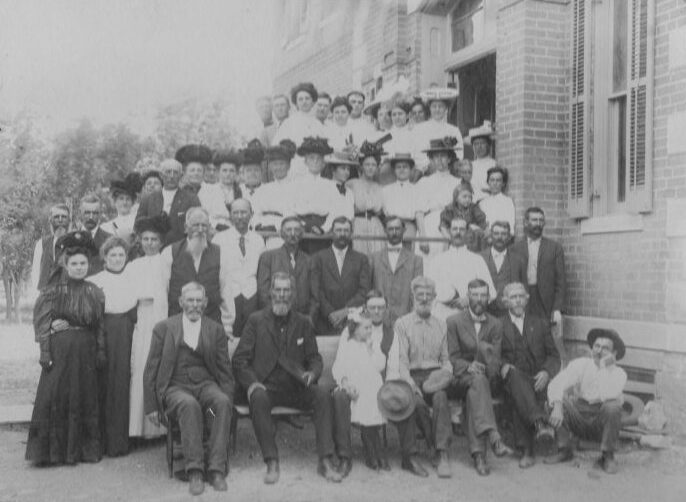
There had been numerous floods in the Ark River Valley before 1965, but the flood that ravaged Kansas, Colorado and New Mexico in June of that year was labeled a 100-year-flood or a once-in-a-lifetime flood. The catastrophic event was the by-product of torrential rains that began on the eastern slope of Colorado’s Rocky Mountains on Monday, June 14 and continued for three days. Many of Colorado’s streams began to flood, including East Plum Creek which joined the equally swollen Plum Creek at Sedalia about 20 miles south of Denver. Their combined waters demolished bridges and swept houses off their foundations. Floodwaters reached the South Platte River then began spreading over open farmland. The Clay, Bijou, Fountain and Purgatory creeks and flooding Platte all rushed towards the Arkansas River, and on the 17th, a 15-foot flood crest struck Pueblo. Gates at John Martin Dam were closed to trap waters in the early morning hours of June 17, and the reservoir held nearly the entire volume of flood run-off. Still, many of the streams that were flooding were east of the big dam.
Flood waters inundated Holly, Colorado where more than six inches of rain fell overnight and caused the raging river to expand even more as it headed further east. Granada also sustained heavy damage. The flood crossed into Kansas early on June 17, and more heavy rain exacerbated the issue. Water from six to eight feet deep filled homes south of the Santa Fe Railroad tracks at Coolidge. The flood stretched more than 1.5 miles across by the time it reached Syracuse where one home was moved a half-mile from its foundation, four others were destroyed and a total of 100 were affected in varying degrees.
The turbulent tides raced towards Kendall, and the rain just kept falling. Residents there were spared the damage because the water never crossed the protective railroad dike at the south boundary of the berg. Miraculously, the approaches to the Kendall bridge were not cut out, but nearby rural residents were not as fortunate. Whole herds of cattle were carried away, and numerous farm homes fell victim. The normally dry Bear Creek also went on a rampage, and the water soon spilled out of the hills into farmland west of K-25. Several sections of roads and highways in Kearny, Grant and Hamilton counties were washed out by Bear Creek water.
In the early morning hours on June 18th, 45-year-old Emanuel “Bud” Weldon, a ranch hand at the Bar-HK Ranch five miles southwest of Lakin, drowned in the high waters. Bud and five others were attempting to flee the area in a pickup after doing what they could to get livestock to higher ground, but the rapidly rising water engulfed the truck. The men clung to a 25-gallon gas tank that was in the back of the truck and floated until reaching a large tree where three took refuge. One man made it to another tree, and another clung to a gatepost. The men had hold of Bud at first, but the force of the water and his weight made him slip from their grasp. Weldon’s body was recovered two days later by helicopter, and the others in his party were eventually rescued via boat and helicopter.
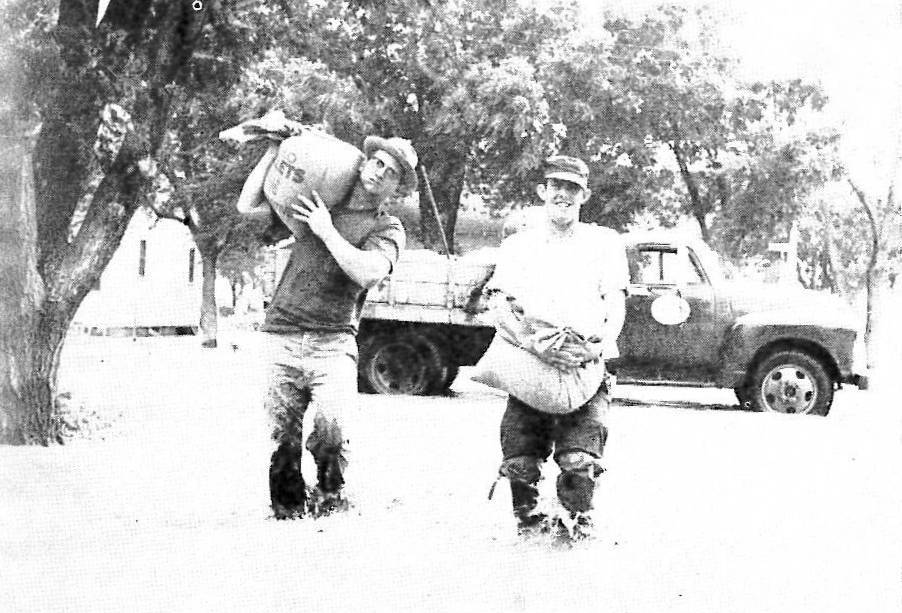
The waters edged into the south side of Lakin around 6:30 a.m. Thursday. Volunteers from all over the community joined forces with city and county employees, the fire department and civil defense to build a dike on the south side of Avenue C. They came with shovels to fill sandbags and with trucks to haul material or do whatever was necessary. As building of the dike progressed, the flood waters were forced to flow east away from town. On the other side of the dike, flood water raced over HWY 25 to a depth of 22 inches. It soon became evident that the highway was acting as a dam. About the time the dike was completed, with permission of the State Highway Department, Gene Hornbaker maneuvered his backhoe around the dike and cut a gash across the road about a quarter of a mile south of the dike which allowed the water to escape on east.
Elderly patients at Lakin’s Sabo manor were evacuated to the Memorial Building in busses, cars and ambulances. Property damage was minimal as most residents who lived south of the tracks had sandbagged around their basement windows. As soon as the dike was completed, county road crews moved their equipment to Deerfield and did revetment work to protect the town. There was no flooding in Deerfield as the water only came up to the railroad tracks, but the south approaches to the river bridges at both Lakin and Deerfield sustained damage. Water poured into Lake McKinney via the Amazon ditch, and the intake at the headgates was badly damaged. State and county health officials ordered the lake closed for all recreational purposes until the first part of July.
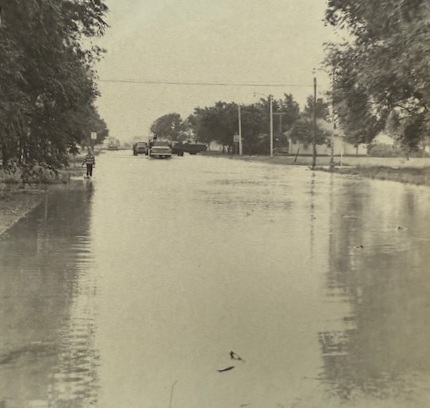
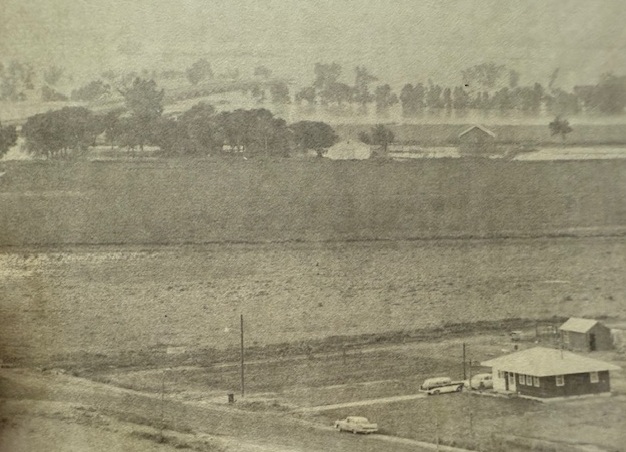
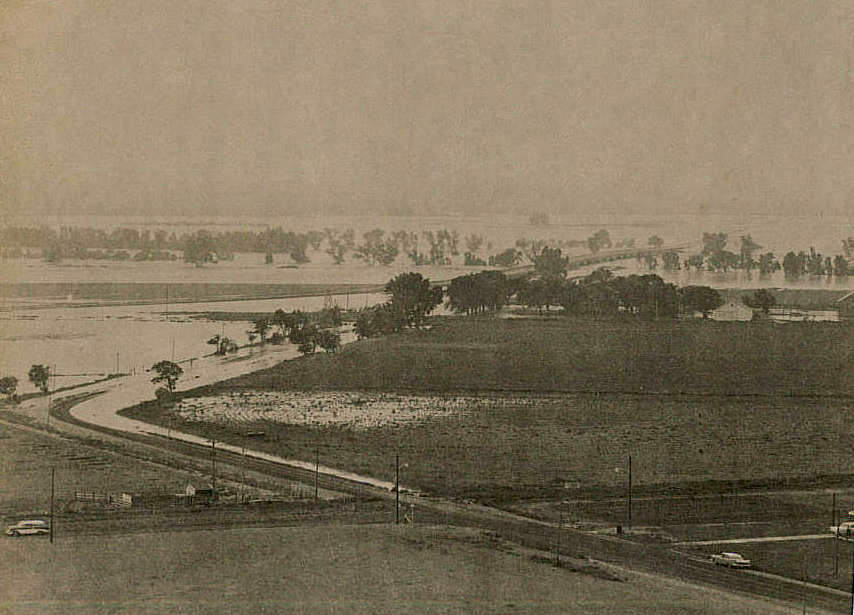
The flood waters had taken on a large amount of debris and dead livestock by the time they reached Finney County. By mid-afternoon on Friday, the swirling waters were seen under the Holcomb bridge, and a few minutes later the bridge was cut off and water was spreading out from the edge of the small community south into the sandhills. On higher ground than the river valley, Holcomb was virtually unharmed. At Garden City, famers trucked loads of dirt and sand to build a 25-block long dike which stood six feet high in some places. Three hundred families were evacuated from the south part of the city where the water reached a depth of 16 feet, and most of the animals at Lee Richardson Zoo were relocated. Flood water backed up through storm sewers, causing serious flooding along Fulton and Chestnut, and some basements north of the tracks filled up. Over $1 million in damage occurred at Garden City, and 24-year-old Jerry Morris drowned when he was swept away as he scrambled toward a tree for refuge south of the Garden City airport.
Pierceville residents were evacuated, and the water rose 15 feet and grew to a mile width in half an hour at Ingalls. Cimarron homes and businesses south of the railroad tracks received extensive damage. A 1/2-mile wide sheet of water rose from 3.8 to 17.2 feet in 15 minutes at Dodge City Saturday morning, and about 1,500 residents in south Dodge left their homes. Boats and helicopters were kept busy in rescue and supply operations. The following day, six feet of water was coursing through some of the homes, and 615 residences and 155 businesses at Dodge City and Wilroads Gardens were damaged. The flood waters reached Kinsley June 21 where highways from three directions were blocked by gushing waters of the Arkansas River and Coon Creek. Dikes at Larned and Great Bend prevented serious damage in those communities, but the surrounding rural area looked like a swamp.
The Department of the interior reported 14 drownings and at least two other deaths resulting from the storms and activities related to what many consider the worst flood in Kansas history. Millions of dollars of damage was done in Kansas, Colorado and New Mexico, and the laborious task of cleaning up began as soon as the waters started to recede.
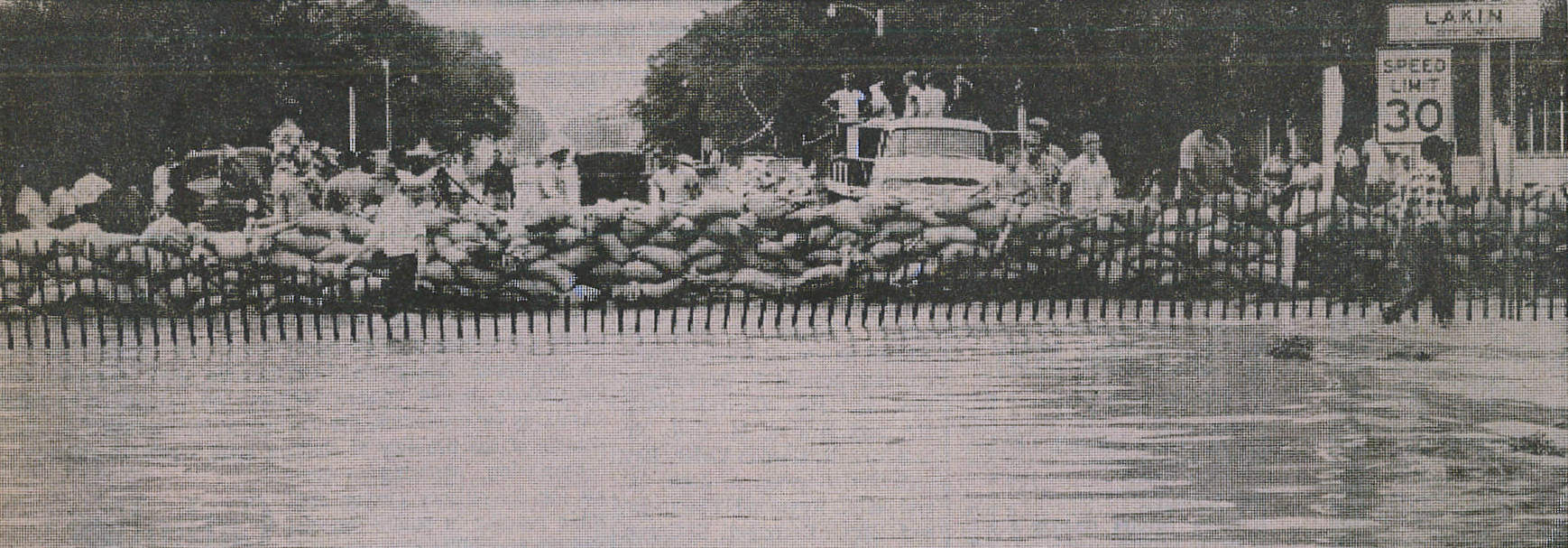
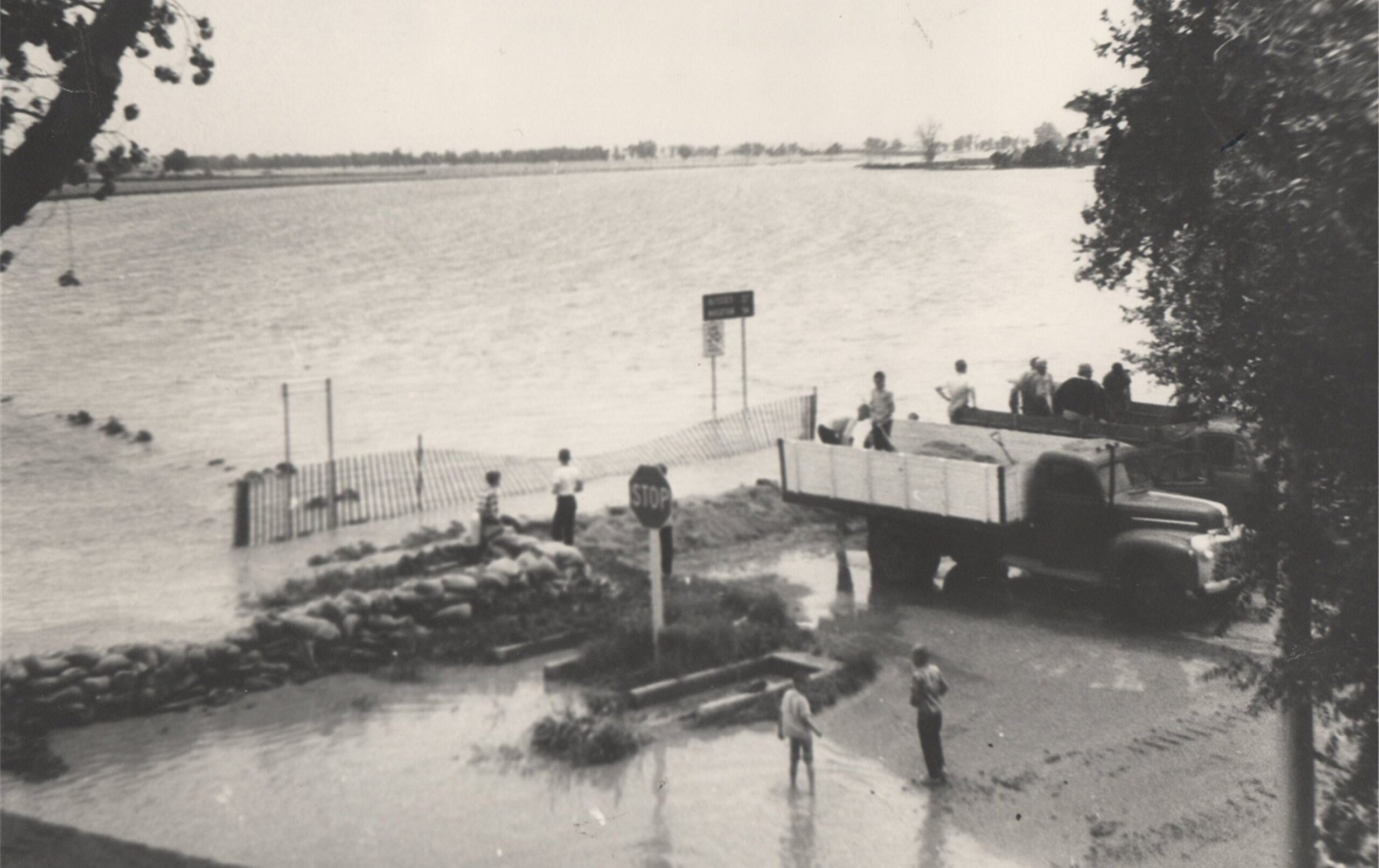
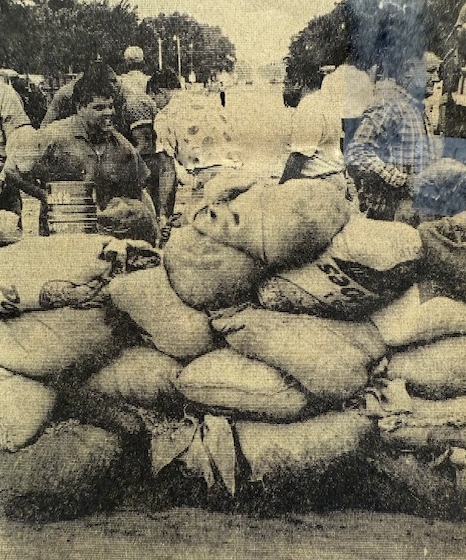











SOURCES: U.S. Dept. of Interior; National Weather Service; History of Kearny County Vol. II; archives of the Lakin Independent, Hutchinson News, Garden City Telegram, and Wichita Eagle; and museum archives.








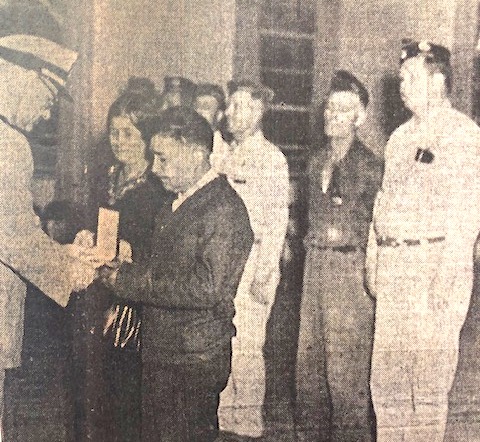
 Tony was awarded the Air Medal for distinguishing himself by meritorious acts and demonstrating heroism while participating in flight operations, and in May of 1946, he was honored with the Purple Heart for military merit and for wounds received in action which resulted in his death. In 1950, Tony’s parents accepted his Distinguished Flying Cross medal in a ceremony at the Veterans Memorial Building. The honor was bestowed for Tony’s heroism and extraordinary achievement as an air-crewman in Patrol Bombing Squadron 101 during operations against enemy Japanese forces from June 1 to October 23, 1944. “Gonzalez rendered invaluable assistance to his pilot in carrying out hazardous long-range attacks against hostile planes, shipping and ground installation in the face of anti-aircraft fire and aerial opposition…Gonzales, by his skill and courageous devotion to duty throughout this period, upheld the highest traditions of the United States Naval Service. He gallantly gave his life for his country.”
Tony was awarded the Air Medal for distinguishing himself by meritorious acts and demonstrating heroism while participating in flight operations, and in May of 1946, he was honored with the Purple Heart for military merit and for wounds received in action which resulted in his death. In 1950, Tony’s parents accepted his Distinguished Flying Cross medal in a ceremony at the Veterans Memorial Building. The honor was bestowed for Tony’s heroism and extraordinary achievement as an air-crewman in Patrol Bombing Squadron 101 during operations against enemy Japanese forces from June 1 to October 23, 1944. “Gonzalez rendered invaluable assistance to his pilot in carrying out hazardous long-range attacks against hostile planes, shipping and ground installation in the face of anti-aircraft fire and aerial opposition…Gonzales, by his skill and courageous devotion to duty throughout this period, upheld the highest traditions of the United States Naval Service. He gallantly gave his life for his country.”













